MODAL OF DEDUCTION
Los
verbos modales must, can´t, might/may/could se utilizan para expresar certeza,
probabilidad o imposibilidad.
POSIBILIDADES:
Utilizamos
estos modales could, might, may para
expresar que algo es posible en un futuro, aunque no estamos seguros de que
ocurra.
NOTA: El verbo siempre va
en su forma base.
- It could rain tomorrow.
- She might come back later.
- We may go to Ibiza next year
- I might play tennis tomorrow though it depends on how I feel.
- My friend could be about 32 I think.
IMPOSIBILIDAD:
Utilizamos
el modal can't/cannot, couldn't/could
not, es decir, can en la forma negativa, para expresar la imposibilidad, ya
sea en el presente o en el pasado.
- Good books can't be short.
- Marla couldn't be on time for the class.
- My roommate can't be at the church, he's not a religious man.
REAL
O PROBABLE:
Usamos
el modal must y should para mostrar
que estamos seguros de algo y que tenemos razones para creerlo así.
- She has been working all day, she must be tired.
- You must have heard the bad news about the accident.
- She finishes work not so she should arrive here any moment.
- The store must be closed at this time.
- It's nearly midnight. They should have arrived by now.
TAG QUESTIONS
Para formar esta pregunta corta se utiliza el auxiliar de la frase principal y su sujeto pero de signo contrario. Si no tuviera auxiliar entonces utilizaríamos el auxiliar “to do”.
Si la oración es afirmativa, la pregunta coletilla es negativa y viceversa.
Oraciones
Afirmativas
(El verbo auxiliar en el "tag" es negativo.) |
Oraciones
Negativas
(El verbo auxiliar en el "tag" es afirmativo.) |
To be
|
|
You're
a teacher, aren't you?
|
You aren't a teacher, are you?
|
He's tired, isn't he?
|
He isn't tired, is he?
|
Tiempo Presente
|
|
You
speak English, don't you?
|
You don't speak English, do you?
|
He swims, doesn't he?
|
He doesn't swim, does he?
|
Tiempo Pasado
|
|
He
went to school, didn't he?
|
He didn't go to school, did he?
|
Presente Perfecto
|
|
You
have finished, haven't you?
|
You haven't finished, have you?
|
He
has left, hasn't he?
|
He hasn't left, has he?
|
Futuro
|
|
She
will cook, won't she?
|
She won't cook, will she?
|
AFIRMATIVAS:
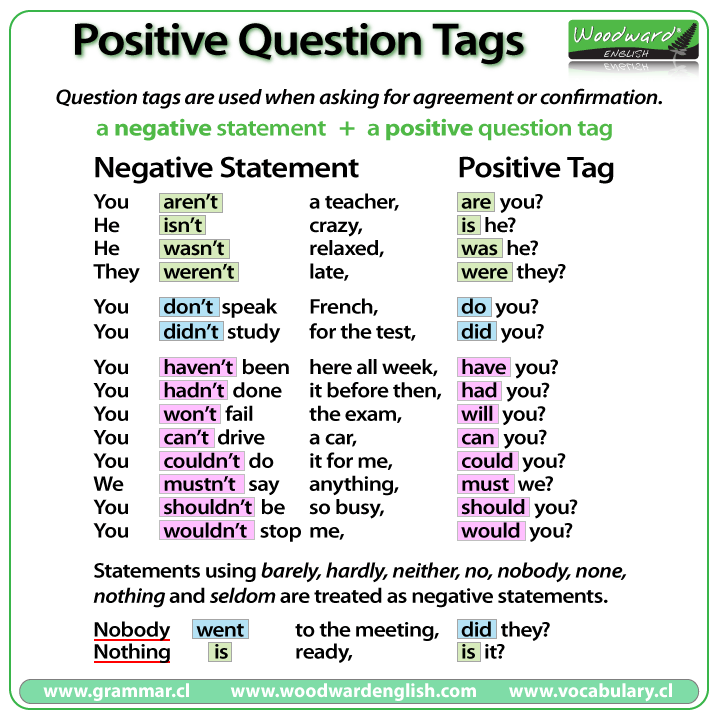
- Your brother is older than you, isn’t he?
- You can help me, can’t you?
- John is getting married, isn’t he?
- You worked yesterday, didn’t you?
- Sarah likes ice cream, doesn’t she?
- You’re not from here, are you?
- Kate’s not American, is she?
- Peter never liked Susan, did he?
- They didn’t go to class yesterday, did they?
- You can’t dance, can you?






